1 . Introduction
2 . My Setup
3 . What is Fern WiFi Cracker?
4 . Why use Fern WiFi Cracker?
5 . How to use Fern WiFi Cracker?
6 . Summary
This post is designed to introduce you to the tool Fern WiFi Cracker.
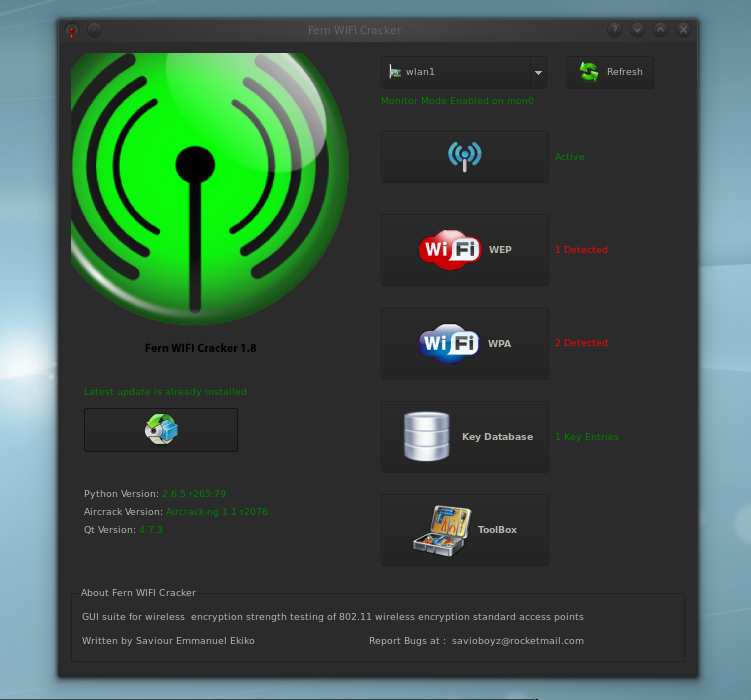
1. Introduction
Welcome to the forty-ninth blog post of 100 tools in 100 days.
Find Fern WiFi Cracker @ GitHub here.
2. My Setup
For running the Fern WiFi Cracker tool, I used Kali Linux in a VMware Workstation 16 Player virtualized environment.
For my network card, I used an Alfa Network AWUS036NHA USB card in monitor mode.
For my victim network, I am using a private Linksys WRT54GL router broadcasting a 2.4Ghz SSID.
For my wordlist I am using a top 4800 WPA list from SecLists found here.
You can find that exact card on Amazon here: https://www.amazon.com/Alfa-AWUS036NHA-Wireless-USB-Adaptor/dp/B004Y6MIXS
Note: For you to use Fern WiFi Cracker you will need a wireless card that has monitor mode.
The majority of wireless cards do not have monitor mode.
Please see an article here on monitor capable wireless cards.
3. What is Fern WiFi Cracker?
If you were around on Day 004 of this blog series I discussed the tool Kismet which is a wireless network detector, sniffer, wardriver, and WIDS.
Fern WiFi Cracker tool is a tool that functions similarly to Kismet, except this tool is used just for attacking WiFi networks.
4. Why use Fern WiFi Cracker?
Some penetration tests require an analyst to connect directly to an organization’s wireless network in order to gain initial or extended access.
Fern WiFi Cracker automates that process in a GUI supported tool which makes getting into protected wireless systems easier. This tool uses wordlists to perform dictionary attacks against the SSID after deauthorizing a MAC address.
Disclaimer: Please only use Fern WiFi Cracker on wireless networks you have explicit legal access to. Attempting to steal your neighbor’s internet is ILLEGAL.
5. How to use Fern WiFi Cracker?
First, you must have a wireless card that supports monitor mode, see section 2 of this post if you are unsure.
Second, Fern Wifi Cracker comes with Kali Linux so no installation is needed during this blog.
In order for this attack to work, you must have a wordlist with the password. This is not always viable or realistic, but for default and weak credentials, this attack method may work. I used the shuffle command to display a random line from the wordlist file, the password chosen for this test was fishhead.

Step 1:
Navigate to your applications menu and to the section:
'06 - Wireless Attacks'
Click "fern wifi cracker"
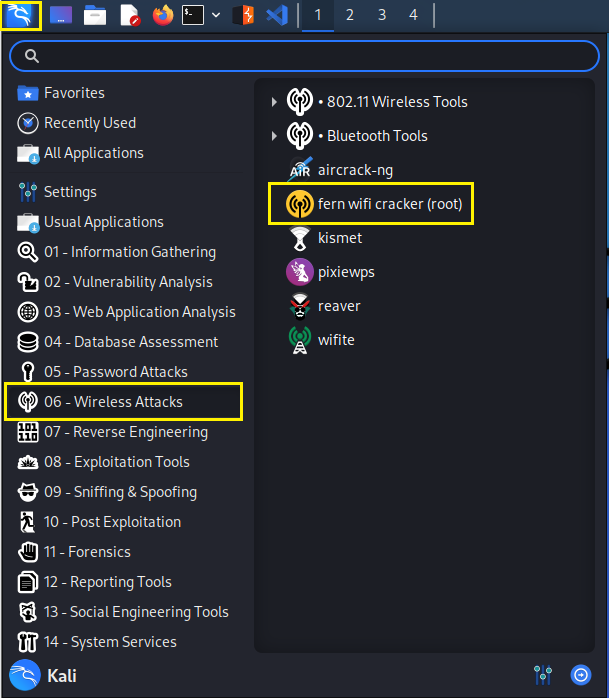
Step 2:
If you are not roo enter your root password in the prompt.
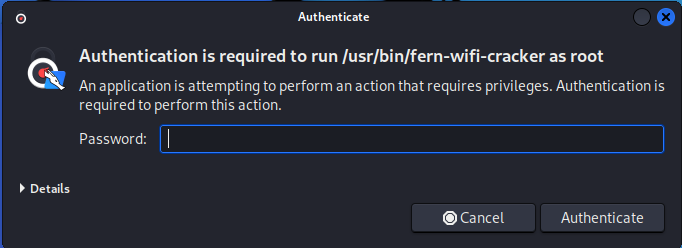
Step 3:
The GUI will open and you are presented with an option to select
your interface network device. Select your wireless card with
monitor and injection capabilities, likely wlan0.
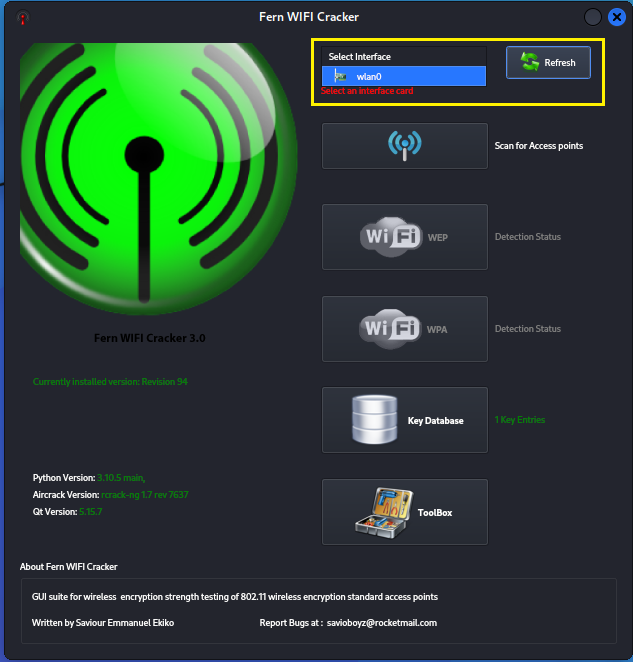
Step 4:
Click the blue wireless signal button to activate scanning mode
for discovering nearby wireless access points.
Once you see XX detected click either WPA or WEP to view the
SSID's found.
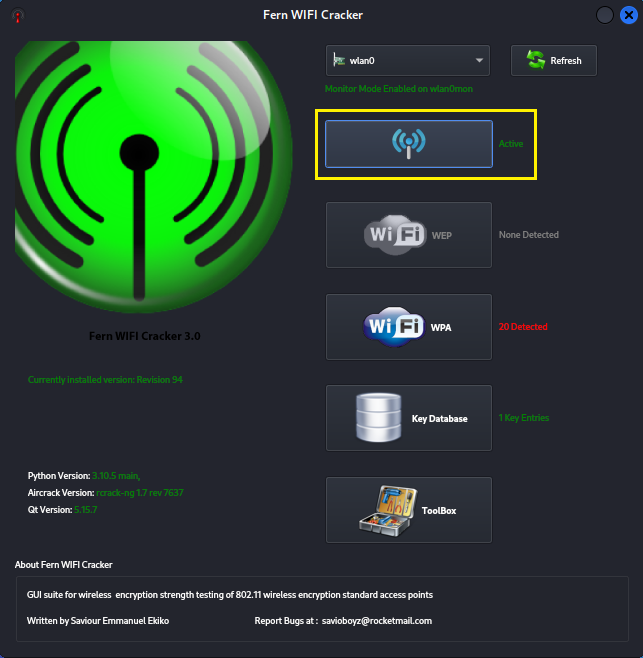
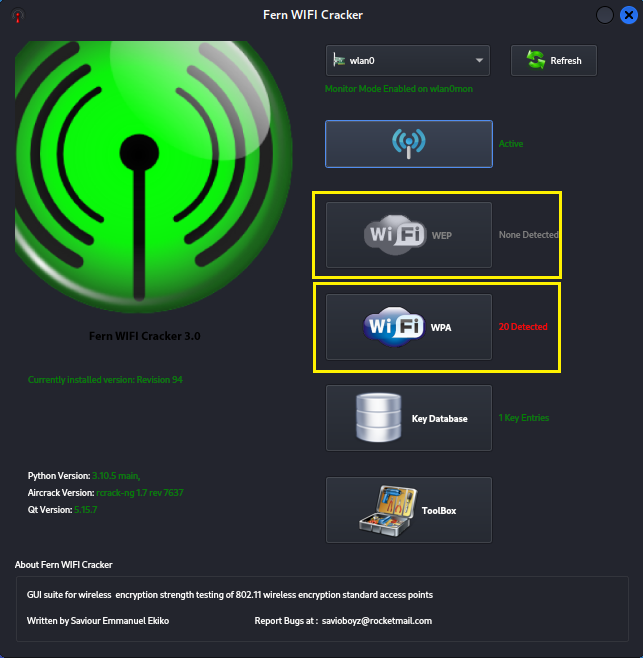
Step 5:
This is the attack menu, click the target access point and click
browse to select a wordlist file for the dictionary attack.
I chose the top 4800 WPA list from SecLists.
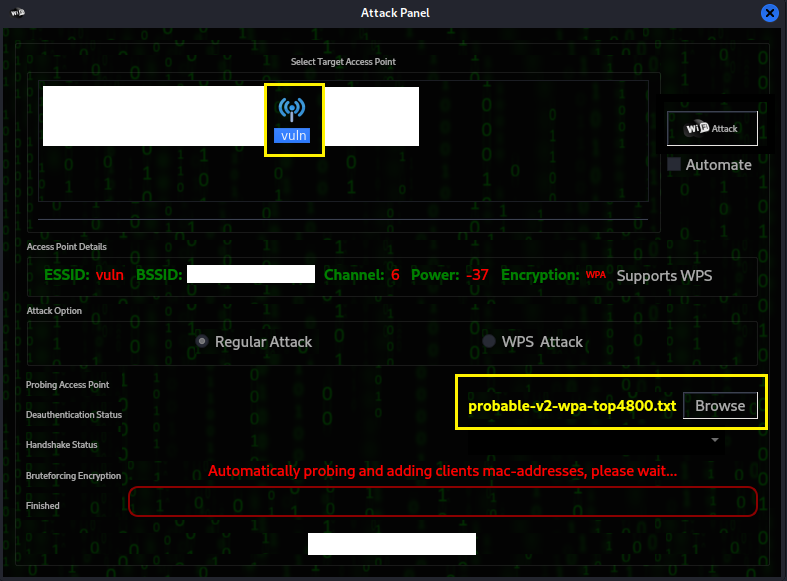
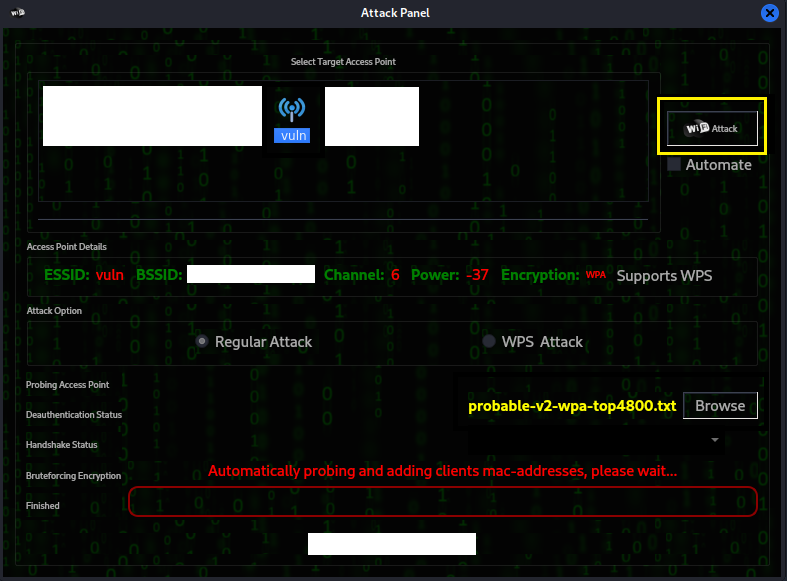
Step 6:
Once ready click attack in the top right of the window. This will
initiate a probe to find MAC addresses currently connected. Then
the tool will attempt a deauthentication process in order to
appear as the MAC address of the deauthenticated device in order
to initiate a handshake to the wireless access point.
Step 7:
Once the handshake is complete the tool will initiate the
dictionary attack and if successful will display the password and
connect to the network.
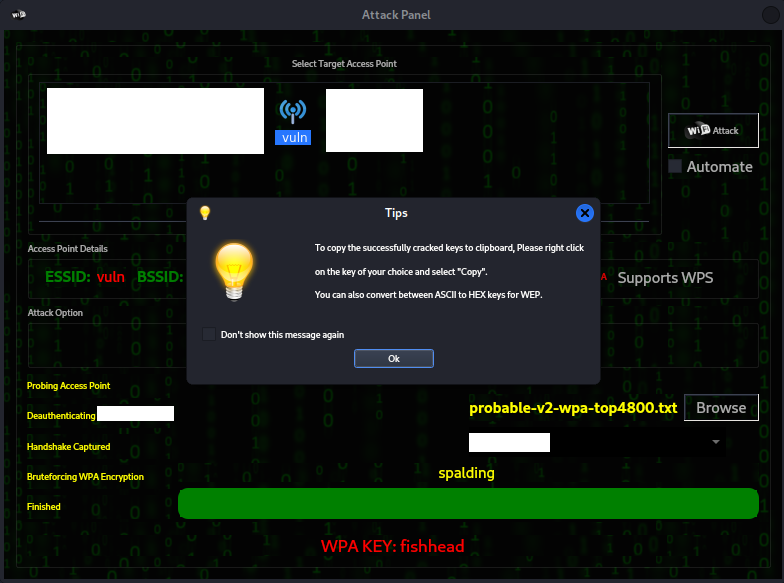
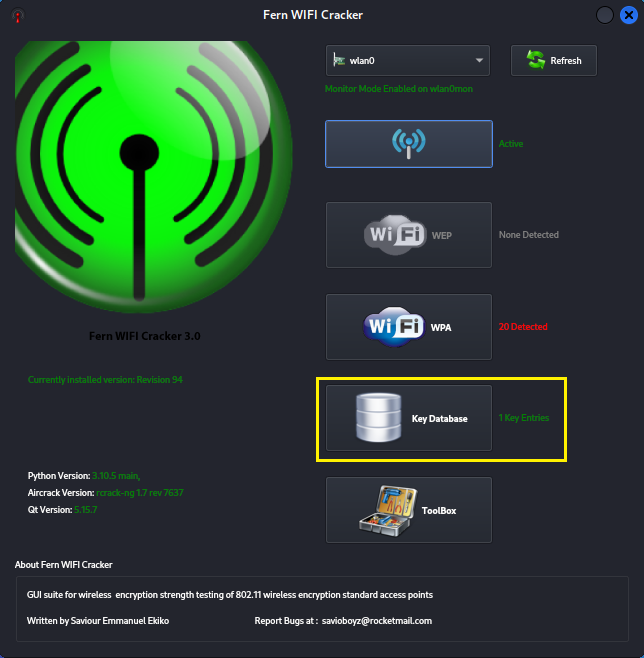
Step 8:
If you want to view previously cracked access points and their
passwords click 'Key Database' on the original menu.
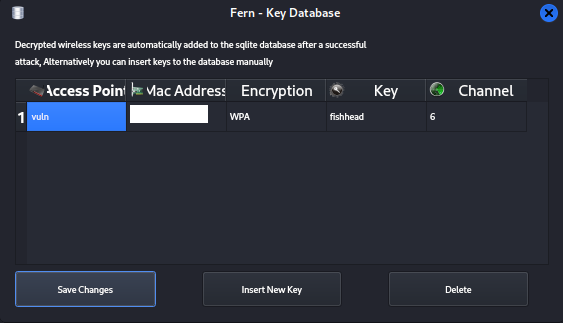
6. Summary
Fern WiFi Cracker does exactly as it sounds, it performs MAC address sniffing on a wireless network, deauthenticates the chosen device, clones the MAC address, and attempts to perform a handshake with the access point.
Once a handshake is established the tool then performs a dictionary attack against the access point in order to gain access to the network.
I hope you enjoyed this blog post.
Thanks for reading!
If you have suggestions for what tool to cover next, contact me!